Introduction
The Indian railway map is a testament to the country's incredible connectivity and vast transportation network. India boasts one of the largest and busiest railway systems globally, serving millions of passengers and transporting an array of goods every day. In this article, we'll delve into the details of the Indian railway map, covering its history, structure, popular routes, and various essential aspects that every traveler and enthusiast should know.
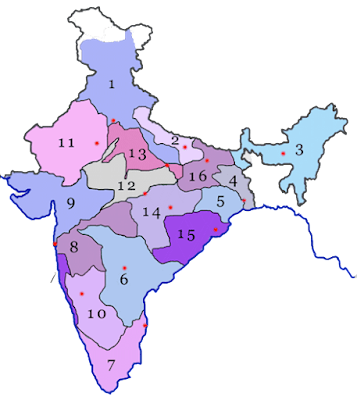
Note: Click on Zone name to get map.
| Sl. No. | Zone | Divisions | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Northern Railway (NR) | Delhi, Ambala, Firozpur, Lucknow, Moradabad | New Delhi (Est. 1952) |
| 2 | North Eastern Railway (NER) | Izzatnagar, Lucknow, Varanasi | Gorakhpur (Est. 1952) |
| 3 | Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) | Alipurduar, Katihar, Rangiya, Lumding, Tinsukia | Guwahati (Est. 1958) |
| 4 | Eastern Railway (ER) | Howrah, Sealdah, Asansol, Malda | Kolkata (Est. 1952) |
| 5 | South Eastern Railway (SER) | Kharagpur, Adra, Chakradharpur, Ranchi | Kolkata (Est. 1955) |
| 6 | South Central Railway (SCR) | Secunderabad, Hyderabad, Guntakal, Guntur, Nanded | Secunderabad (Est. 1966) |
| 7 | Southern Railway (SR) | Chennai, Tiruchirappalli, Madurai, Palakkad, Salem, Thiruvananthapuram | Chennai (Est. 1951) |
| 8 | Central Railway (CR) | Mumbai, Bhusawal, Pune, Solapur, Nagpur | Mumbai (Est. 1951) |
| 9 | Western Railway (WR) | Mumbai, Vadodara, Ahmedabad, Ratlam, Rajkot, Bhavnagar | Mumbai (Est. 1951) |
| 10 | Southern Western Railway (SWR) | Hubballi, Bengaluru, Mysuru | Hubballi (Est. 2003) |
| 11 | North Western Railway (NWR) | Jaipur, Ajmer, Bikaner, Jodhpur | Jaipur (Est. 2002) |
| 12 | West Central Railway (WCR) | Jabalpur, Bhopal, Kota | Jabalpur (Est. 2002) |
| 13 | North Central Railway (NCR) | Allahabad, Agra, Jhansi | Prayagraj (Allahabad) (Est. 2003) |
| 14 | South East Central Railway (SECR) | Bilaspur, Raipur, Nagpur | Bilaspur (Est. 2003) |
| 15 | East Coast Railway (ECoR) | Khurda Road, Waltair, Sambalpur | Bhubaneswar (Est. 2003) |
| 16 | East Central Railway (ECR) | Danapur, Dhanbad, Mughalsarai, Samastipur, Sonpur | Hajipur (Est. 2002) |
| 17 | Konkan Railway Corporation Limited (KRCL) | NA | Navi Mumbai (Est. 1998) |
I
Indian Railways has a fascinating history dating back to 1853 when the first passenger train chugged between Bombay (now Mumbai) and Thane. The British colonial rulers established this 34-kilometer line, marking the beginning of India's vast railway journey. Since then, Indian Railways has grown by leaps and bounds, connecting remote villages to bustling cities and becoming an integral part of the nation's growth.
The Structure of Indian Railways
The Indian railway network is organized into 18 railway zones, each headed by a General Manager. These zones are further divided into divisions, ensuring effective management and operation. The zonal divisions are responsible for maintaining and upgrading tracks, stations, and infrastructure within their jurisdiction.
Gauge Diversity in India's Railways
India's railway network features a diverse range of gauges, including Broad Gauge, Meter Gauge, and Narrow Gauge. The broad gauge, with a track width of 1,676 mm, is the most widely used, covering about 65% of the total route. Understanding the different gauges is essential for comprehending the rail map.
Major Railway Zones
The Indian railway map can be broadly divided into seven major zones, each catering to specific geographical regions. These zones include Northern, Eastern, Western, Southern, Central, South Eastern, and North Eastern Railway zones. Each zone operates and manages various routes and services within its territory.
High-Speed Railways in India
India is embarking on ambitious high-speed rail projects, aiming to revolutionize train travel with trains reaching speeds of up to 350 km/h. The Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail (MAHSR) corridor, modeled on Japan's Shinkansen, is one such groundbreaking project set to transform the railway experience.
Popular Tourist Routes
The Indian railways offer a plethora of scenic and culturally rich routes for tourists. The Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, Nilgiri Mountain Railway, and the Palace on Wheels are some iconic journeys that take passengers through breathtaking landscapes and historical wonders.
Technological Advancements in Railways
Indian Railways has embraced technology to enhance passenger experience and operational efficiency. From online ticket booking to GPS-based tracking systems for trains, technology has revolutionised how we interact with the railways.
The Indian Railway Budget
The allocation and utilisation of funds are critical for the development and maintenance of railways. Understanding the railway budget and its impact on various projects is crucial for the continuous growth of the railway network.
Cargo and Freight Services
Apart from passenger services, Indian Railways also plays a vital role in transporting goods and freight across the country. The railways offer cost-effective and efficient freight services that aid in the nation's economic growth.
Eco-Friendly
Indian Railways is actively working towards adopting eco-friendly practices, including the use of solar power, rainwater harvesting, and waste management. These initiatives contribute to reducing the environmental impact of railway operations.
Safety Measures and Security
Ensuring the safety of passengers and railway assets is a top priority for Indian Railways. The railways have implemented various safety measures, including modern signaling systems, surveillance cameras, and dedicated security personnel.
Famous Railway Stations
Indian railway stations are not just functional hubs but architectural gems that reflect the country's heritage and history. Stations like Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus and Howrah Junction are iconic landmarks with stunning designs.
Heritage Trains of India
Heritage trains provide a nostalgic journey back in time. The Palace on Wheels and the Deccan Odyssey are luxury trains that offer royal experiences reminiscent of the past.
Future Expansion Projects
Indian Railways continues to invest in expansion projects to connect more regions and improve transportation. Upcoming projects like the Bullet Train and dedicated freight corridors promise to revolutionise rail travel in India.
Indian Railways and Culture
Indian Railways is an integral part of the nation's culture, as it facilitates the movement of people and goods across the diverse landscape of India. It has inspired literature, movies, and art that showcase its impact on the country's cultural fabric.
Railway Museums in India
For railway enthusiasts, visiting railway museums is a delightful experience. Museums like the National Rail Museum in Delhi house a vast collection of vintage locomotives, carriages, and artifacts that narrate the story of Indian Railways.
Railway Budget Allocation Impact
The allocation of funds in the railway budget directly affects the progress of various railway projects and services. Analyse how budgetary decisions impact the growth and modernization of Indian Railways.
Iconic Railway Bridges
Indian Railways boasts some awe-inspiring railway bridges, such as the Chenab Bridge and Pamban Bridge. These engineering marvels exemplify the railway's commitment to overcoming geographical challenges.
Role of Indian Railways in National Development
Indian Railways plays a significant role in the country's development by fostering economic growth, connecting remote areas, and supporting industries through efficient transportation.
FAQs
1.Is the Indian railway network the largest in the world?
Yes, Indian Railways is the world's largest railway network in terms of route length, carrying over 23 million passengers daily.
2. Are the heritage trains safe for travel?
Yes, heritage trains are well-maintained and equipped with modern safety features, ensuring a safe and memorable journey.
3. Can I book Indian railway tickets online?
Yes, Indian Railways offers a convenient online booking platform through the IRCTC website and mobile app.
4. Which is the longest train route in India?
The Vivek Express, running from Dibrugarh in Assam to Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu, holds the record for the longest train journey in India.
5. Are there dedicated trains for tourists in India?
Yes, India has several luxury tourist trains like the Maharajas' Express and the Golden Chariot that offer a regal travel experience.
6.What are the major challenges faced by Indian Railways?
Indian Railways faces challenges such as capacity constraints, maintenance of aging infrastructure, and ensuring passenger safety.