Table of contents
Introduction
In the realm of modern electric rail transport, the pantograph stands as a pivotal component, seamlessly integrating power collection and delivery for electric locomotives. This article delves into the functionality, advantages, and intricacies of the electric locomotive pantograph, highlighting its indispensable role in contemporary Indian rail systems.
What is the pantograph of Electric Locomotive?
The pantograph of an electric locomotive is a device mounted on the roof of the train designed to collect electrical power from overhead wires mounted on equipment known as overhead equipment(OHE). It plays a crucial role in the operation of electric trains by providing the necessary electrical connection to power the train’s motors and systems. Here’s a breakdown of its key features and functions.

Key Features and Functions of a Pantograph
Power Collection: The primary function of a pantograph is to collect electrical power from an overhead contact wire, known as a catenary. The pantograph maintains continuous contact with this wire as the train moves.
Contact Strip: At the top of the pantograph is a contact strip, often made of carbon or metalized carbon, which slides along the overhead wire to draw electricity. This material is chosen for its good conductivity and durability.
Spring-Loaded Mechanism: The pantograph is spring-loaded to ensure that the contact strip maintains consistent pressure against the overhead wire. This helps to provide a stable electrical connection despite the movement and vibrations of the train.
Raising and Lowering: Pantographs are designed to be raised and lowered. This is typically achieved using compressed air systems, which are also connected to the train’s braking system. The pantograph is raised to make contact with the overhead wire and lowered when not needed or when passing through sections of track without overhead wires.
Electrical Insulation: Support insulators electrically isolate the pantograph from the train’s body to prevent electrical current from passing through the train’s structure, which could pose safety risks.
Stabilization: Components like the guiding rod and coupling rod help stabilize the pantograph, ensuring it moves smoothly and maintains proper alignment with the overhead wire.
How does pantograph work?
Pantographs are typically operated by compressed air from the locomotive’s braking system. This compressed air is used either to raise the pantograph and hold it against the conductor wire or, when springs are used, to lower it. In the latter case, a catch holds the arm in the down position as a precaution against loss of air pressure. Additionally, for high-voltage systems, the compressed air supply helps extinguish electric arcs when roof-mounted circuit breakers are used.
What are types of pantograph?
Pantographs come in two primary designs:
- Single-Arm Pantographs: These are lighter and require less power to operate, making them ideal for modern high-speed trains.
- Double-Arm Pantographs: Heavier and more robust, these pantographs offer increased fault tolerance, making them suitable for freight and heavy-duty locomotives.
What is the structure of a pantograph?
The structure of a pantograph for an electric locomotive is a complex assembly designed to ensure reliable and efficient power collection from overhead wires. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the main components and their functions:
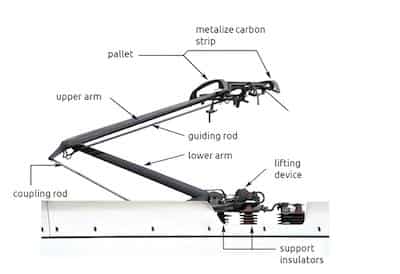
Contact Strip (Metalized Carbon Strip): This is the topmost component of the pantograph that comes into direct contact with the overhead wire. It is typically made of carbon or a carbon-metal composite to provide good electrical conductivity and minimize wear on both the strip and the wire.
Pallet: The pallet supports the contact strip and ensures even pressure distribution against the overhead wire. It acts as a stable base for the contact strip.
Upper Arm: The upper arm connects the pallet to the rest of the pantograph structure. It is a crucial component for maintaining the vertical position of the contact strip against the overhead wire.
Guiding Rod: The guiding rod stabilizes the movement of the pantograph, ensuring smooth and consistent operation. It helps align the upper and lower arms, contributing to the overall stability and functionality of the pantograph.
Lower Arm: The lower arm links the guiding rod and the upper arm to the base of the pantograph. It provides support and helps manage the vertical motion of the pantograph.
Coupling Rod: The coupling rod connects the lower arm to the base structure of the pantograph. It plays a role in the mechanical movement and stability of the pantograph assembly.
Lifting Device: The lifting device is typically operated by compressed air and is responsible for raising and lowering the pantograph. It ensures that the pantograph maintains the correct pressure against the overhead wire. When the pantograph is not in use or when passing through sections without overhead wires, the lifting device can lower it.
Support Insulators: These insulators are mounted at the base of the pantograph and serve to electrically isolate the pantograph from the locomotive’s body. They prevent the electrical current from passing through the train’s structure, ensuring safety and proper electrical operation.
What is the advantage of pantograph?
The key advantage of pantograph is as follows:
Higher Voltage Handling: Pantographs can handle higher voltages compared to third-rail systems, making them suitable for high-speed and long-distance rail services.
Efficiency: Overhead wire systems enable efficient power transmission over long distances with minimal power loss.
Safety: Overhead systems reduce the risk of electrical accidents compared to third-rail systems, which are more exposed and pose a greater risk of accidental contact.
FAQ
Q.is pantograph AC or DC?
A.Pantographs can be used for both AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) systems, depending on the design of the railway electrification system.
Q.why carbon strips are used in pantograph?
A.Carbon strips are used in pantographs for good thermal conductivity , low wear & tear, self lubricating and several important reasons that contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of electric trains.
Conclusion
The electric locomotive pantograph is a marvel of modern engineering, playing a crucial role in the efficient and safe operation of electric trains. By ensuring a steady and reliable power supply, pantographs enable trains to achieve higher speeds and cover longer distances with improved energy efficiency. As rail transport continues to evolve, the pantograph remains a key component in the pursuit of sustainable and high-performance rail systems
